WASTE WATER TREATMENT BY ELECTRONIC TECHNOLOGY
INTRODUCE
Wastewater treatment by electrolysis technology is a method of applying electrochemical processes, to remove pollutants in wastewater under the action of electric current, through soluble and insoluble electrodes.
The advantage of electrolysis technology is that it does not use chemicals, does not use adsorbents and does not create waste streams. Basically, wastewater treatment by electrolysis technology includes: electrocoagulation EC (Electrocoagulation) and electrochemical oxidation EO (Electrooxidation).
EC . ELECTRICAL COACATOR TECHNOLOGY
(Electrocoagulation Technology)
Electrochemical coagulation EC can be defined as an electrochemical process in which pollutants are coagulated by the oxidation of dissolved anode electrode, colloidal particles after the electrochemical reaction will easily separated from water by conventional settling, filtration and flotation methods. EC is a process that uses an electrochemical reaction that has the same basis as conventional coagulation but differs in that it uses an electric current to induce the reaction. Both processes aim to destabilize colloidal particles in the wastewater. However, in the normal coagulation process, coagulant chemicals such as aluminum salts or iron salts will be used. For electrolytic coagulation, the coagulant will be generated from the metal ion dissolved at the anode anode. When metal ions are released into wastewater, they produce highly reactive metal hydroxides to coagulate pollutants in wastewater. During processing, the anode will gradually corrode, so after a period of use it is necessary to replace the new electrode plate.
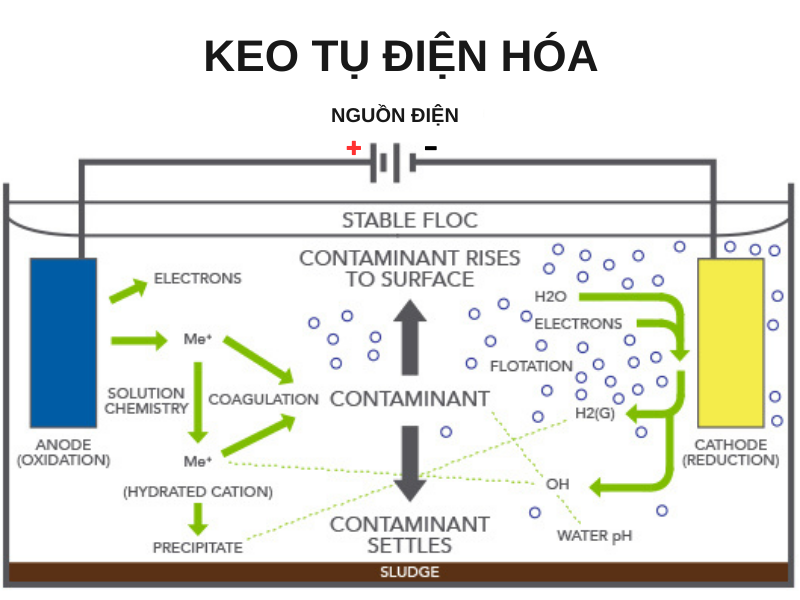
The reactions take place in the electrolytic bath
At the anode, electrolysis of the aluminum or iron electrode will occur the following reactions: Al → Al3+ + 3e Fe → Fe2+ + 2e- The aluminum and iron cations produced combine with OH- ions present in the water. form aluminum or iron hydroxides according to the following reaction equations: Al3+ + 3OH- → Al(OH)3 Fe2+ + 2OH- → Fe(OH)2 At the cathode in the electrolytic bath, dehydration occurs. into hydrogen bubbles: H2O + 2e- → H2 + 2OH- These metal hydroxides will participate in polymerization reactions: Al(OH)3 → (OH)2Al-O-Al(OH)2 + H2O Fe(OH)2 → (OH)Fe-O-Fe(OH) + H2O These polymers can remove pollutants by adsorption, complexation or precipitation.
Advantages of electrocoagulation technology
- No chemicals are used
- Reduce operating costs
- Does not take up much space and construction area
- Waste sludge generated is less than conventional physicochemical flocculation
- Color removal up to 95%, COD and BOD removal up to 70%
ELECTRONIC CHEMICAL OXIDATION TECHNOLOGY EO
(Electrooxidation Technology)
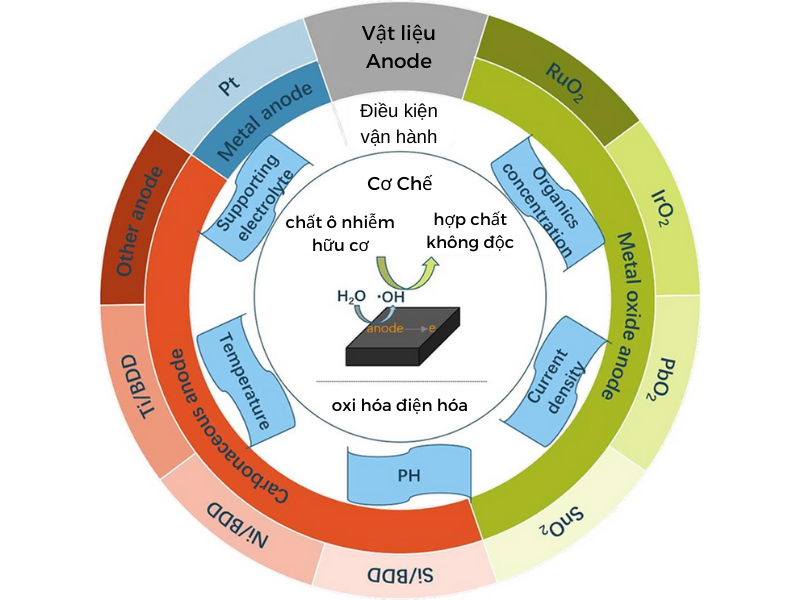
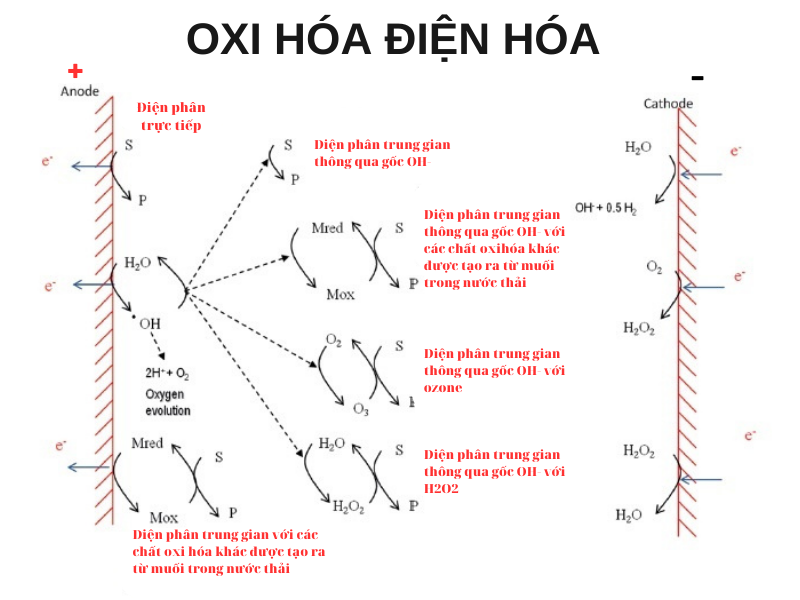
Is an electrochemical process also known as electrochemical higher order oxidation (EAOP). EO uses selected electrodes (non-corrosive anodes), the treatment process generates hydroxyl radicals (strong oxidizing agents) that can remove organic pollutants and other impurities. biodegradation. Oxidative electrochemical reactions can be divided into two groups:
- Oxidation takes place directly on the electrode surface
- Indirect oxidation through OH- radicals with oxidizing agents in wastewater.
Electrolytic oxidation will depend mainly on the anode material. Common anode materials are: boron-doped diamond (BDD), graphite-coated titanium, metal oxides: PbO2, SnO2, Sb2O3. Because these substances have the ability to increase the oxidation potential.