WASTE WATER TREATMENT BY AFB . BOILIZED GAS TECHNOLOGY
INTRODUCE
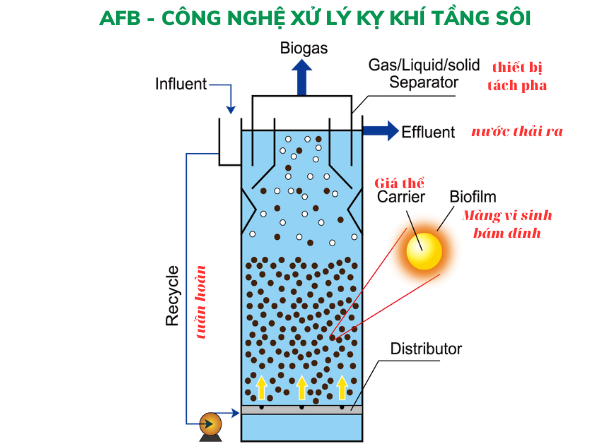
AFB (Anaerobic Fluidized Bed (AFB)) anaerobic biological treatment technology uses small substrates (such as sand and activated carbon) as a medium for microbial growth (vsv). The media provide a large surface area for anaerobic or anoxic microorganisms to attach to. Wastewater flow is distributed from the bottom up, creating a fluidized bed state with a sludge buffer layer of microorganisms growing. Wastewater flow should be controlled and combined with recirculation flow. So that the weight of the media particles is equal to the resistance caused by the wastewater. As a result, the height of the fluidized bed is stabilized. The depth of the fluidized bed ranges from 4 to 6 m. Normally, a small substrate particle size of 0.3 – 0.8 mm is used. The velocity of upstream wastewater is from 10-30 m/h. The goal is for the substrate particles to expand 100%. Circulatory currents are also the main agents that transport food sources for microorganisms. The wastewater interacts with the sludge bed to help VSV grow below the ideal mass transfer rate.
BENEFITS OF AFB . FLUIDED GAS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
- Suitable for low concentration wastewater mainly wastewater with dissolved COD and wastewater containing bioinhibitory components.
- AFB can operate under high hydraulic loads.
- Treatment with high concentration of activated sludge in the tank, large load.
- The treatment tank has a narrow and tall shape, saving the use area.
APPLICATION
- Wastewater from chemical industry: acrylic pulp, polyester fiber, polyester tree vinegar, petroleum resin (phenolic, amino, acid alcohol ester), high nitrateconcentration
- Wastewater from slaughterhouse
- Wastewater from the food industry: Dairy products, beverages