COLOR DEVELOPMENT SOLUTION
What is color? Why deal with chroma?
In wastewater treatment, pollution indicators need to be treated such as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), solids, suspended particles, metals and other factors. Color is also an important factor to be considered. So what is color? Are there methods to handle chroma? Wastewater containing high color is usually wastewater from the textile, dyeing and printing industries. tanning, paper making… Most of the dyes encountered in wastewater have polycyclic aromatic structures containing elements such as nitrogen, metals and sulfur, making it difficult to treat wastewater by other methods. physics, chemistry and biology. The following are effective methods of color treatment that have been applied, you can refer to to know the outstanding characteristics of each method.
1- Coagulation method
- Chemical flocculation: application of flocculation process, using chemicals to separate pollutants with color into slurry and settle. Chemicals used to create the flocculation reaction are PAC, AlCl3, FeCl2,…… in which PAC is the most widely used because of its high efficiency and ease of storage and use. However, this method consumes a lot of chemicals, generates a lot of sludge and is expensive to treat.
- Electrochemical coagulation: Electrochemical coagulation (electrolysis) is the use of electrodes immersed in water under the effect of DC current. The anode anode will corrode and dissolve into the wastewater solution, the commonly used electrode is aluminum or iron, the dissolved ions will react with the pollutant similar to chemical coagulation and form sludge. sedimentation to separate pollutants from wastewater. The advantage of this method is that it consumes less chemicals, produces less sludge, and is capable of oxidizing other difficult-to-treat pollutants.
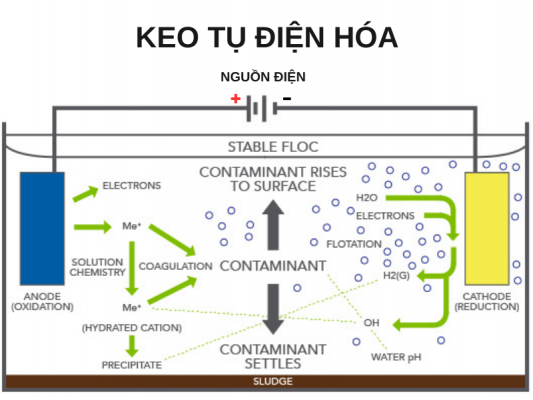
See also: Waste water treatment by electrolysis technology
2- Adsorption method
Adsorption is a very popular method for decolorization. The materials with good adsorption capacity are activated carbon, zeolite, activated aluminium, silica gel and polymeric adsorbents… In essence, activated carbon has the ability to absorb color and odor very well. Not only does it help reduce color, it also helps reduce unpleasant odors. However, this approach is only applicable to small wastewater treatment systems. Besides, the cost of activated carbon is also quite high compared to other wastewater treatment chemicals.

3- Membrane method
The principle of operation of this method is to pass the wastewater through a semi-permeable membrane. The semi-permeable membrane allows only water to pass through and retains pollutants, insoluble organic matter including color and suspended solids. Some commonly used wastewater filtration membranes are nanofiltration membranes, RO reverse osmosis membranes, microfiltration membranes, ultrafiltration membranes, etc. Currently, nanomembrane technology is synthesized using semiconductor materials capable of adding photocatalytic properties (ZnO-cellulose acetate, TiO2-graphene, TiO2-pvdf… etc.) with the ability to remove color completely.
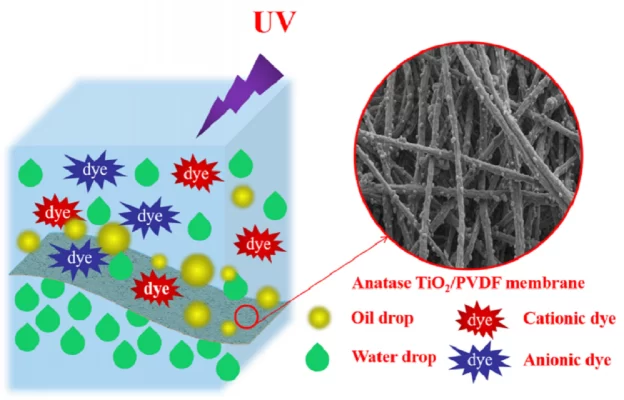
However, this method requires high investment and operating costs, so it is rarely applied to wastewater treatment.
4 – Advanced oxidation method
Advanced oxidation is the most effective method to treat wastewater with difficult coloration. Usually applied at the end of the treatment stage after the wastewater has undergone physical, chemical, biological treatment steps…
- Ozone method
Ozone with the chemical formula O3 consists of 3 oxygen atoms bonded together. Compared to another stable form of oxygen, O2, the O3 molecule has more than one oxygen atom. This oxygen atom also has the least stable bond in the molecule, it is easy to split to become a free oxygen atom. This is also the reason why Ozone is a very strong oxidizing agent, stronger and safer than chlorine. Most of the dyes encountered in wastewater have polycyclic aromatic structures containing elements such as nitrogen, metals and sulfur, making it difficult to treat wastewater by physical, chemical and biological methods. learn. The conjugated chains present in the dye structure, the colorant, are actively destroyed by ozonation. Using ozonation as a treatment technique is beneficial because no sludge is generated. Decomposition of the dye is achieved in a single step and furthermore, ozone decomposes to oxygen which helps to increase DO in the water. However, ozonation rarely occurs complete oxidation, so there is a disadvantage of forming by-products.
- Fenton’s method
This is a technological method of oxidizing difficult-to-biodegrade organic matter, which has the ability to effectively decolorize. The method of using iron ions as a hydrogen peroxide catalyst to oxidize organic substances by generating free radicals with high oxidizing capacity has a wide range of applications. Therefore, Fenton is considered as the optimal method in treating wastewater with difficult coloration.
- Fenton uniform
The traditional fenton method uses a combination of H2O2 and Fe2+ iron salts to generate a free hydroxyl radical OH* which is a strong oxidizing agent capable of degrading colorants and other difficult-to-treat substances, while Fe2+ is oxidized. turned into Fe3+. The Fenton reaction equation is written as follows: Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + OH- + OH• The •OH radical after formation will participate in the oxidation reaction of organic compounds present in the water to be treated: conversion of substances. organic matter from high to low molecular weight organic substances CHC (high molecular weight) +•HO → CHC (low molecular weight) +CO2 +H2O+ OH-
- Heterogeneic Fenton – FBR Fenton
The most important disadvantage of the homogeneous Fenton process is that it has to be performed at low pH, and for the solution to turn into a colloidal precipitate it is necessary to raise the pH > 7. Therefore, the cost of chemicals is very high. Therefore, to overcome the disadvantages of iron used as a catalyst, there have been many research works to replace it with Goethite iron ore (FeOOH), iron-containing sand, or iron on Fe/SiO2, Fe/TiO2 carriers. , Fe/activated carbon, Fe/Zeolite… this process is similar to the Fenton process studied above, so it is called a heterogeneous Fenton-type process. The Fenton reaction is initiated by the production of Fe(II) in the presence of H2O2, the reduction-dissolution of goethite occurs. then there is a re-precipitation of Fe(III) back to goethite. This process can be represented in the following steps: alpha-FeOOH(s) + 2H+ + ½ H2O2 –> FeII + 1/2O2 +2H2O FeII + H2O2 —> Fe(III) + •HO +OH- Fe( III) + H2O+OH- –> alpha-FeOOH(s) + 2H+ The heterogeneous Fenton process has been successfully researched and developed with FBR-Fenton technology (Liquid Fenton) with FeOOH catalyst for reduction results. high color and has been applied in Vietnam. FBR-Fenton will be a potential technology in the future to remove difficult-to-treat wastewater such as color and persistent organic matter.
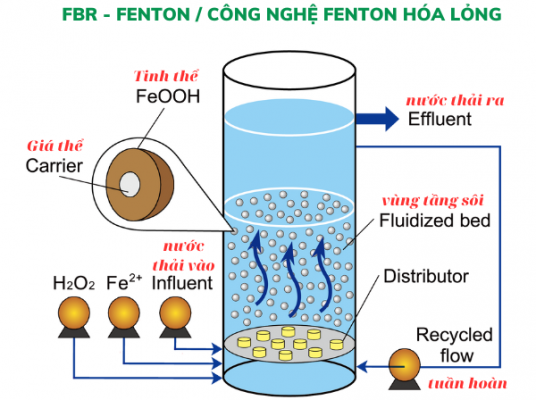
Use FBR-Fenton for color processing
See also: FBR Fenton Technology
TiO2 .-based photocatalysis
TiO2 or titanium photocatalysis is a process that uses light energy to activate titanium catalysts to generate OH* radicals (strong oxidizing radicals) that decompose organic substances, colorants into non-toxic or non-toxic forms. mineralizes to CO2 + H2O. This process is a natural process, does not use chemicals and has no negative impact on the environment.
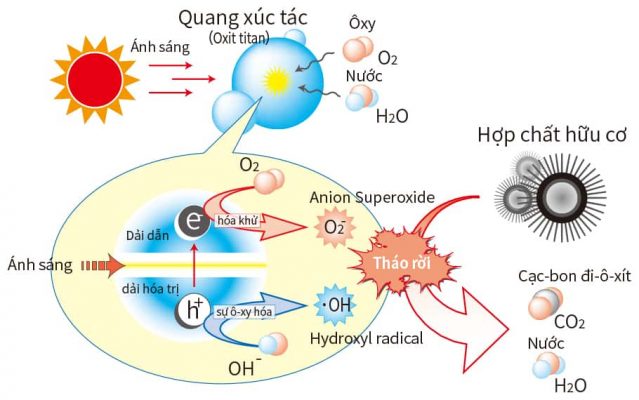
See also: Titanium photocatalyst technology
MPTEK specializes in providing solutions to treat color in wastewater by advanced AOPs advanced oxidation processes. Contact us now for advice and find the best solution for you! MPTEK SOLUTION COMPANY LIMITED Hotline: 0903188563 Address: 20 Huynh Thien Loc, Hoa Thanh Ward, Tan Phu District, HCMC.


